This page is no longer being updated
This page is no longer being updated
For the latest updates and information, please refer to our new Dewey documentation page at docs.deweydata.io
The information for this page can be found on this page:
There was an upgrade in Dewey API to v3 from v2. This tutorial reflects the v3 API with additional convenience functionalities. I tried to maintain the tutorial as close to the v2 tutorial. Python version tutorial is available here.
1. Create API Key
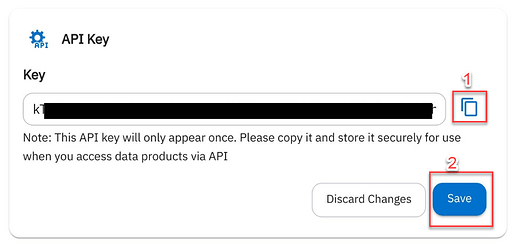
In the system, click Connections → Add Connection to create your API key.
As the message says, please make a copy of your API key and store it somewhere. Also, please hit the Save button before use.
2. Get a product path
Choose your product and Get / Subscribe → Connect to API then you can get API endpoint (product path). Make a copy of it. You will notice that the path now includes “v3” instead of “v2”.
3. R Code
Beginning November 12, 2023, R library for Dewey Data (deweydatar) is available on GitHub (Dewey-Data/deweydatar (github.com)). You can install the library directly from the GitHub source as following. It requires devtools.
# Load "devtools" library (install it first, if don't have it)
library(devtools)
# Install deweydatar package from GitHub
install_github("Dewey-Data/deweydatar")
# Use deweydatar library
library(deweydatar)
# Start using functions...
# Example, not run
apikey_ = "Your API Key"
pp_ = "Your product path (API endpoint)"
files_df = get_file_list(apikey_, pp_, print_info = T)
download_files(files_df, "C:/Temp")
deweydatar package has the following functions:
get_file_list: gets the list of files in a data.frameread_sample_data: read a sample of data for a file download URLread_sample_data0: read a sample of data for the first file with apikey and product pathread_local_data: read data from locally saved csv.gz filedownload_files: download files from the file list to a destination folderdownload_files0: download files with apikey and product path to a destination folderslice_files_df: slicefiles_df(retrieved byget_file_list) by date range
All the update of the R functions and new features will be supported through the library starting November 12, 2023.
Below is the raw R code you can copy and run. This is deprecated and there will be no more support on this code. Here is the R code for file downloads (for API v3).
library(httr2)
make_api_endpoint = function(path) {
if(!startsWith(path, "https://")) {
api_endpoint = paste0("https://app.deweydata.io/external-api/v3/products/", path, "/files")
return(api_endpoint)
} else {
return (path)
}
}
# Get the list of files on server
get_file_list = function(apikey, product_path,
start_page = 1, end_page = Inf,
print_info = T) {
product_path = make_api_endpoint(product_path)
data_meta = NULL
page_meta = NULL
files_df = NULL
page = start_page
while(T) {
req = request(product_path) %>%
req_headers("X-API-KEY" = apikey) %>%
req_headers("accept" = "application/json") %>%
req_url_query ("page" = page)
response = tryCatch(
{
req_perform(req)
}, warning = function(cond) {
message("Warning during httr2::req_perform.")
message(cond)
message("")
}, error = function(cond) {
message("Error during httr2::req_perform.")
message(cond)
message("")
}
)
if(is.null(response)) {
return(NULL)
} else if(response$status_code == 401) {
print(response);
return(NULL);
}
# resp_content_type(response)
# resp_status_desc(response)
res_json = resp_body_json(response)
# initialize
if(res_json$page == start_page) {
data_meta = data.frame(
total_files = res_json$total_files,
total_pages = res_json$total_pages,
total_size = res_json$total_size/1000000,
expires_at = res_json$expires_at
)
}
message(paste0("Collecting files information for page ", res_json$page, "/",
res_json$total_pages, "..."))
if(!is.null(res_json$partition_column)) {
partition_column = res_json$partition_column
} else {
partition_column = NA
}
page_meta = rbind(page_meta,
data.frame(page = res_json$page,
number_of_files_for_page = res_json$number_of_files_for_page,
avg_file_size_for_page = res_json$avg_file_size_for_page/1000000,
partition_column = partition_column)
)
col_names_str = names(res_json$download_links[[1]])
dn_link_unlist = unlist(res_json$download_links)
# When partition column (key) is null
if(!is.null(res_json$partition_column)) {
dn_link_df = data.frame(matrix(dn_link_unlist, ncol = length(col_names_str), byrow = T))
} else {
dn_link_df = data.frame(matrix(dn_link_unlist, ncol = length(col_names_str)-1, byrow = T))
dn_link_df = data.frame(dn_link_df[, 1], NA, dn_link_df[2:ncol(dn_link_df)])
}
colnames(dn_link_df) = col_names_str
page_files_df = data.frame(page = res_json$page, dn_link_df)
files_df = rbind(files_df, page_files_df)
page = res_json$page + 1
if((page > res_json$total_pages) | (page > end_page)) {
message("Files information collection completed.")
break
}
}
# To date type
files_df$partition_key = as.Date(files_df$partition_key)
# Attach index
files_df = data.frame(index = 1:nrow(files_df), files_df)
# Backward compatibility
files_df$download_link = files_df$link
if(print_info == T) {
message(" ")
message("Files information summary ---------------------------------------")
message(paste0("Total number of pages: ", data_meta$total_pages))
message(paste0("Total number of files: ", data_meta$total_files))
message(paste0("Total files size (MB): ", round(data_meta$total_size, digits = 2)))
message(paste0("Average single file size (MB): ",
round(mean(page_meta$avg_file_size_for_page), digits = 2)))
message(paste0("Date partition column: ", page_meta$partition_column[1]))
message(paste0("Expires at: ", data_meta$expires_at))
message("-----------------------------------------------------------------")
message(" ")
}
#return(list(files_df = files_df,
# data_meta = data_meta, page_meta = page_meta));
return(files_df)
}
# Read URL data into memory
read_sample_data = function(url, nrows = 100) {
# if(nrows > 1000) {
# message("Warning: set nrows no greater than 1000.");
# nrows = 1000;
# }
url_con = gzcon(url(url), text = T);
df = read.csv(url_con, nrows = nrows, skipNul = TRUE, encoding = "UTF-8");
return(df);
}
# Read first file data into memory
read_sample_data0 = function(apikey, product_path, nrows = 100) {
files_df = get_file_list(apikey, product_path,
start_page = 1, end_page =1, print_info = T);
message(" ");
if(!is.null(files_df) & (nrow(files_df) > 0)) {
return(read_sample_data(files_df$link[1], nrows));
}
}
# Can be slow. Recommend to use fread function at data.table package.
read_local_data = function(path, nrows = -1) {
df = read.csv(gzfile(path), nrows = nrows);
return(df);
}
# Download files from file list to a destination folder
download_files = function(files_df, dest_folder, filename_prefix = NULL, skip_exists = TRUE) {
dest_folder = gsub("\\", "/", dest_folder, fixed = T);
if(!endsWith(dest_folder, "/")) {
dest_folder = paste0(dest_folder, "/");
}
# number of files
num_files = nrow(files_df);
for (i in 1:num_files) {
message(paste0("Downloading ", i, "/", num_files,
" (file index = ", files_df$index[i], ")"))
file_name = paste0(filename_prefix, files_df$file_name[i]);
dest_path = paste0(dest_folder, file_name)
if (file.exists(dest_path) && skip_exists) {
print(paste0("File ", dest_path, " already exists. Skipping..."))
next
}
message(paste0("Writing ", dest_path))
message("Please be patient. It may take a while...")
req = request(files_df$link[i])
response = req_perform(req)
file_con = file(dest_path, "wb")
writeBin(response$body, file_con)
close(file_con)
message(" ")
}
}
# Download files with apikey and product path to a destination folder
download_files0 = function(apikey, product_path, dest_folder, filename_prefix = NULL) {
files_df = get_file_list(apikey, product_path, print_info = T);
message(" ");
download_files(files_df, dest_folder, filename_prefix);
}
# Slice files_df for specific data range of from start_date to end_date.
# For example, start_date = "2023-08-14", end_date = "2023-08-21".
slice_files_df = function(files_df, start_date, end_date = NULL) {
start_date = as.Date(start_date)
if(is.null(end_date)) {
end_date = Inf
}
end_date = as.Date(end_date)
sliced_df = files_df[(start_date <= files_df$partition_key) &
(files_df$partition_key <= end_date), ]
return (sliced_df)
}
4. Examples
I am going to use Advan weekly pattern as an example.
# API Key
apikey_ = "Paste your API key from step 1 here."
# Advan product path
product_path_= "Paste product path from step 2 here."
You will only have one API Key while having different product paths for each product.
You can now see the list of files to download by
files_df = get_file_list(apikey_, product_path_, print_info = TRUE);
files_df;
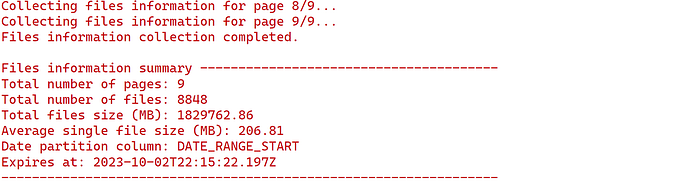
print_info = TRUE set to print the meta information of the files like below:
Advan weekly pattern data has a total of 8848 files over 9 pages, a total of 1.8TB, and 206.81MB average file sizes.
API v3 introduced the “page” concept that files are delivered on multiple pages. Each page includes about 1,000 files. So, if the data has 8848 files, then there will be 8 pages with 1,000 files each and the 9th page with 848 files. Thus, if you want to download files on pages 2 and 3, you can
files_df = get_file_list(apikey_, product_path_,
start_page = 2, end_page = 3, print_info = T);
Also, you can do this to download files from page 8 to all the rest
files_df = get_file_list(apikey_, product_path_,
start_page = 8, print_info = T);
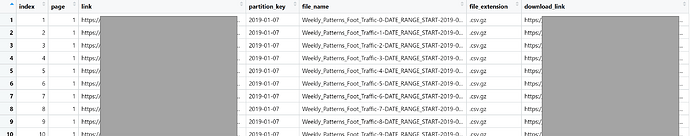
files_df includes a file list (data.frame) like below:
The data.frame has
indexfile index ranges from 1 to the number of filespagepage of the filelinkfile download linkpartition_keyto subselect files based on datesfile_namefile_extensionfile_size_bytesmodified_atdownload_linkwhich is the same as thelink(download_linkis left there to be consistent with the v2 tutorial).
You can quickly load/see a sample data by
sample_data = read_sample_data(files_df$link[1], nrows = 100);
This will load sample data for the first file in files_df (files_df$link[1]) for the first 100 rows. You can see any files in the list.
If you want to see the first n rows of the first file skipping get_file_list, you can use
sample_data = read_sample_data0(apikey_, product_path_, nrows = 100);
This will load the first 100 rows for the first file of Advan data.
Now it’s time to download data to your local drive. First, you can download all the files by
download_files0(apikey_, product_path_, "E:/temp", "advan_wp_")
The third parameter is for your destination folder (“E:/temp”), and the last parameter (“advan_wp_”) is the filename prefix. So, all the files will be saved as “advan_wp_xxxxxxx.csv.gz”, etc. You can leave this empty or NULL not to have a prefix.
The second approach to download files is to pass files_df:
download_files(files_df, "E:/temp", "advan_wp_")
This will show the progress of your file download like below:
If some of the files are already downloaded and if you want to skip downloading them, set download_files(files_df, "E:/temp", "advan_wp_", skip_exists = TRUE).
Sometimes, the download may stop/fail for any reason in the middle. If you want to resume from the last failure, then you can pass a slice of files_df. The progress shows file index = 2608 for example. If the process was failed on that file, you can resume from that file by
download_files(files_df[files_df$index >= 2608, ], "E:/temp", "advan_wp_")
Also, you may want to download incremental files, not all the files from the beginning. Then you can slice the data by date range. For example, to get the file list that falls between 2023-09-01 to 2023-09-10
sliced_files_df = slice_files_df(files_df, "2023-09-01", "2023-09-10")
and to get files from 2023-09-01 to all onward files
sliced_files_df = slice_files_df(files_df, "2023-09-01")
and then run
download_files(sliced_files_df, "E:/temp2")
You can quickly open a downloaded local file by
sample_local = read_local_data("E:/temp2/advan_wp_Weekly_Patterns_Foot_Traffic-0-DATE_RANGE_START-2019-01-07.csv.gz",
nrows = 100)
Files are large to read from local disk and R’s base read.csv can be slow. I recommend using fread function in the data.table package.
Thanks